Flushing your DNS cache could assist if you’re experiencing trouble seeing particular websites. Here’s what it entails, as well as how to accomplish it on both Windows and Mac.
When your Mac is trying to figure out how to load a page, it uses your DNS cache as a memory.
Although flushing the DNS isn’t tough, the procedure varies with each new os. On the newest macOS versions, we’ll guide you through the procedures to properly reset your DNS.
You might have tried to fix this problem with small fixes like Flush your DNS Cache on Mac, but this approach may not have worked. This post is the tech-savvy solution. Also, we have the best solution for that and this is MacKeeper.
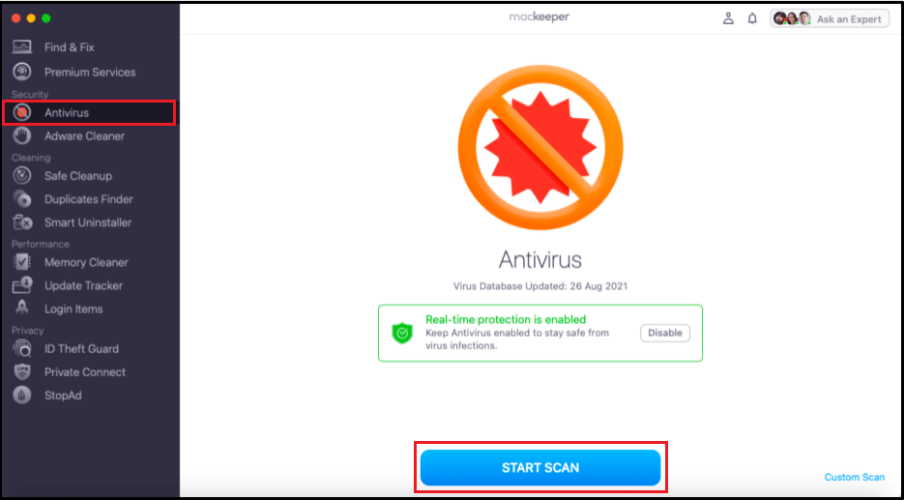
Run a scan to identify any Malware on MacKeeper

Because the cache contains IP addresses for the searched domains, this reduces project load times. Rather than rerouting to DNS servers, the system responds to queries directly from the cache.
The DNS cache is short storage on your PC that stores all of your recent DNS lookups. This allows your browser to resolve these lookups more quickly, reducing the time it takes for a web page to load.
Also Read: Macbook Won’t Charge – Here is How to Fix Macbook Not Charging
Every website you visit has its IP address saved in the DNS cache. Faster connections can be achieved by storing this data in a location where the browser can easily access it. However, flushing your DNS has advantages, such as safeguarding your browser history and assisting with the resolution of certain issues.
For some of the major reasons, you must clean the DNS cache of your Mac.
So if you are not aware of the multiple benefits of cleaning DNS cache from your system, you need to know them for the better health of your system.
Also Read: How to Fix kernel_task High CPU Usage on Mac (2021 Guide)
On a Mac, you’ll need to use the native command-line interface known as Terminal and perform the proper command to clear the DNS cache. Depending on whatever version of macOS you’re using, the procedure differs.
To clear your DNS cache on macOS Big Sur, follow these steps:
The thing to remember: If Spotlight doesn’t open Terminal, go to Go > Utilities > Terminal or click Applications, open the utility folder, and then double-click Terminal.
Also Read: Organize and Optimize Your Mac with these 7 Genius Tips
Older versions of macOS have different commands. This may be helpful to fix websites not loading on Mac. To clear the DNS cache in these earlier versions, do the following commands in Terminal:
Check the affected website after flushing the DNS cache on your Mac to see whether the problem has been resolved and you can access it normally again.
If you’re using a Windows computer, MacKeeper is a Mac cleaner and optimizer app that helps you to clear the clutter on your Mac. You must follow the steps below to remove the DNS cache.

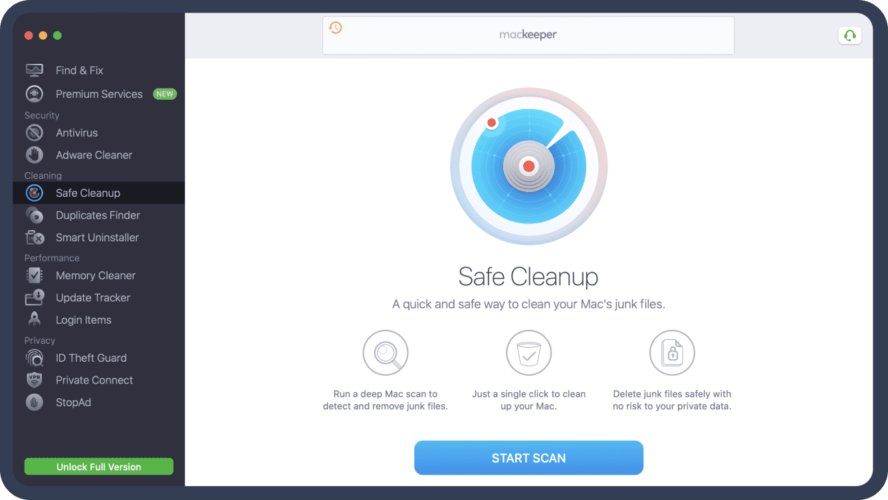
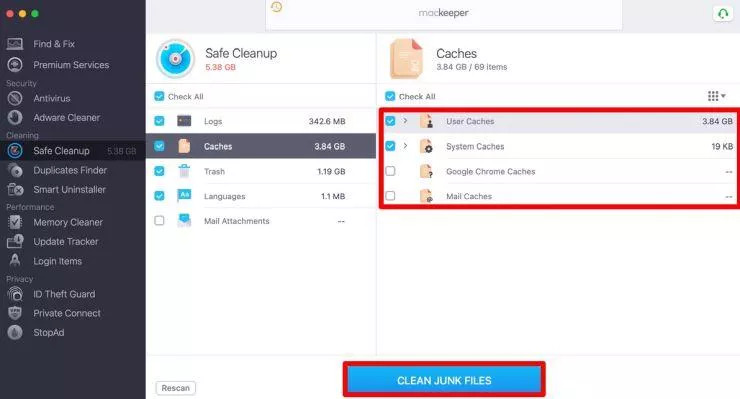
Also Read: How to Uninstall Apps on Mac OS – Delete Apps on Mac
The method of clearing the DNS cache is simple and quick. Almost all Windows systems follow the same method. We’ll be using Windows 10 in the example below.

There is no set time limit, but you may do it as much as you like without harming your Mac.
To verify your Mac’s DNS cache, go to:
Yes, flushing the DNS cache on your Mac is safe. Although cached data is only temporary storage, clearing the DNS cache too frequently hinders it from performing its function of accelerating page loading.
Removing your Mac’s DNS cache helps you defend against cybercriminal manipulation, hide your search history, and fix technical issues with web apps.
Outline: You have got a number of great options to flush your DNS cache on Mac. The great way to make this process more benevolent for you is we have suggested you “MacKeeper”. MacKeeper will surely help you out to get your Mac free from Malware and other crashing issues. Hopefully, you have got the most promising solution to fix the issues of clear DNS cache in this article.
July 21, 2022

December 2, 2021

August 24, 2022
Deprecated: File Theme without comments.php is deprecated since version 3.0.0 with no alternative available. Please include a comments.php template in your theme. in /home/firmsexplorer/public_html/wp-includes/functions.php on line 5613